I have a new book coming out on April 26: Modern Horse Training
The subtitle of the book is: A Constructional Guide to Becoming Your Horse’s Best Friend.

In the clicker training community we’ve been talking a lot recently about constructional training. Dr Jesús Rosales Ruiz has brought to our attention the work of Israel Goldiamond. Dr Goldiamond was a clinical psychologist. Instead of trying to “fix” problem behavior, he constructed new repertoires. The analogy would be instead of trying to fix a falling down, hundred year old barn with a leaky roof, cracked foundations and ceilings that are too low for horses, you build a new barn that’s purpose-built for what you need. It has none of the problems of the falling-down barn. The old barn may still be on your property, but you don’t have to use it for your horses. The old, unwanted behavior may still exist. Nothing is ever erased or unlearned, but there is a clean, new behavior in repertoire that you can call on instead.
The term constructional training appeals to me. I like building things. The idea that we can teach complex behaviors by first breaking them down into smaller component parts is not new to me. My horses showed me this decades ago.
Nor is this a new idea in the horse world. It is how good trainers train. But that doesn’t make it the norm. Far from it. What we see around us are people who confront problems head on. The horse world is full of instructors who tell their students to send their frightened horses forward, to make them obey, to show them who is boss. Sometimes this works and sometimes it puts the rider in the hospital and the horse on a trailer to the auction yards.
My Path to a Constructional Mindset
I have always been horse crazy. Like so many others I grew up in a family that just didn’t share my obsession over horses. My parents did at least provide me with the opportunity to ride. Over time I developed a decent seat. I could ride, maybe not that well, but riding out over rough terrain, riding at speed, riding bareback were all well within my capabilities. As a teenager, I thought I knew how to ride. As a young adult, I decided I was wrong. Yes, I could ride, but I didn’t really know how to ride. There’s a difference. And I certainly didn’t know how to train. I wanted to learn, so I started to take lessons at a local hunter jumper stable. To choose the stable I opened the phone book – yes, this was a time before computers when there were actual phone books with yellow pages directories. When I chose the stable that was closest to my house, I had no idea what I was getting myself into.
The owner had been around horses all of his life. He had grown up poor with very little formal schooling. I’m pretty sure he would not have been able to read the words I’m writing here, but my goodness he could read horses. He was a superb horse person. Talk about horse whisperers – he was definitely one of them.
He was running a hunter jumper barn because that’s where the money was in the northeast, but that wasn’t where he started out. At one point he had been top ten in the country – in bull riding.
That’s certainly not a typical background for a trainer at a jumper barn, at least not in this region. It made for “exciting” lessons. He had no physical fear. And he didn’t understand fear in others, not in people and certainly not in horses. His approach to fences was to go straight at them, the higher the better.
In New York where I live the thoroughbred racing industry is strong. That means if you are looking for a riding horse, you will encounter a lot of thoroughbreds. The horses in the school line were all thoroughbreds with only one exception, and they were all literally off the track. On Sunday the horses would be racing. On Monday they would be on a dealer’s van heading for the riding stable. The dealers knew Pick was looking for cheap horses, horses that weren’t fast enough, or sound enough for the trainers to hang onto, but who might do as riding horses.
These were horses who had never jumped a fence in their lives – at least not with a rider on board. Pick would set up a line of fences. He’d have one of the teenage boys who rode for him get on and they’d send the horse over the jumps. If a horse balked, they would build a chute. Two men would stand on either side of the chute with lunge whips while the rider drove the horse forward with a crop.
When the horse cleared the fence, the rails went up. They wanted to see what the horse could do.
The horses that took the fences down, or that came up lame afterwards were put back on the trailer and were sent back to the dealer’s yard. The others stayed and were put into the school line. I rode some amazingly athletic horses. I also rode some very frightened, unbalanced, and untrained horses. And I learned a lot about brick-wall training.
Brick-wall Training
Brick-wall training refers to an approach to problem solving where you go head-on into the problem. It was the reality I saw at this stable, and it’s a metaphor for much of what we encounter in the rest of society. If there’s a brick wall in front of you, you head over it, no matter how tall or how wide it is. You either make it over, or you crash. Oh well.
Brick-wall problem solving is fine if you are athletic enough, strong enough, sound enough, brave enough to make it over the fence. Many of those thoroughbreds were. But many of the riders weren’t. Pick lost a lot of potentially good riders to broken bones and just plain old fear.
I very quickly decided to opt out of the group lessons. I watched as many as I could, but I chose to take private lessons instead. I wanted to control what I was being taught. I wasn’t interested so much in going over the fences. That was a fun outcome, but only if the fence was jumped well. I wanted to know how to ride a correct corner that would bring me into a balanced approach to the fence. In other words, I was looking for the components that made for a successful ride. Because I had ridden before, I knew what I wanted to learn.
I baffled Pick. He thought riders just wanted to jump. In my lessons I would stop and ask questions. It turned out he knew a lot about balance. If you asked the right questions you could learn a lot from him. I asked a lot of questions, and I did indeed learn a lot about good riding. By watching the group lessons I also learned what I didn’t want.
I couldn’t go straight at brick walls, not with my horse. This was Peregrine’s mother. I bought her from Pick just before she turned a year old. He had bred her to be a racehorse, but he was just as glad to sell her early. She passed a pre-purchase vet check. Now that I’ve seen more pre-purchase exams, I know the vet was pretty superficial with this one. He wasn’t expecting to see any problems in such a young horse so he didn’t look for any. Not long after that exam, I began to see the first small signs that there was something terribly wrong.
At first, I saw her dragging her hind feet. When I asked Pick about it, he said she was just being lazy. How many times since then have I heard people say that about a horse?
When I saw her fall for the first time, I called the vet back in. This time he looked more closely, and he diagnosed her as a wobbler. She had spinal cord damage. When I started asking questions and doing some digging it was clear that the cause was a handling incident that had gone wrong. She was tied tight to a post while a teenager pulled her mane for the first time. She protested. He persisted. She fought back. She was against the four foot kick board of the arena. Her only escape was over the rail so she jumped it with her head tied tight. I’ll leave it to you to imagine the rest of that scene.
The incident occurred shortly before I bought her. I wouldn’t have known anything about it except one of the visible signs of the event was a swollen hind leg. If I hadn’t seen the swelling during one of my visits to the barn, no one would have said anything about it.
The swelling went away, but the damage to her spinal cord remained. The injury left her with limited awareness of her hindquarters. Wobbler syndrome is descriptive even if it doesn’t tell you very much about what has happened internally. It can be caused by injury, and there is also equine protozoal myeloencephalitis (EPM) which at that time was just beginning to be understood. In either case, even the vets at Cornell had no treatment to offer me. My local vet told me I would never be able to ride her, and he advised me to put her down.
I couldn’t do that. I couldn’t end her life simply because I wouldn’t be able to ride her. That wasn’t right. Nor could I afford to retire her to a pasture somewhere while I got a second horse to ride.
The vet told me that her condition would deteriorate over time, and I would eventually be forced to put her down for safety reasons. That was the future I had in front of us, but in the meantime I needed to deal with what she was struggling with on a day by day basis.
For starters she had trouble going in and out of her stall because there was a sill over the threshold that was intended to keep the bedding from spilling out into aisle. I thought if I taught her to go over ground poles, she would have more confidence stepping over the sill. So I set out a round jump pole. That terrified her. She refused to go anywhere near it. I could have forced her over it. That’s the “show them who’s boss” approach to training I had seen modeled all around me at the riding stable. I didn’t want to fight with her, so I took a different approach.
A ground pole was too hard. That was too big a “jump”. I swapped it out for a flat board that wouldn’t roll if she stepped on it. She was still afraid. She couldn’t manage it.
I tried a lead rope. That was still too hard. So then I drew a line in the sand. That she could walk over. From the line in the sand, I reintroduced the lead rope, then the flat board, and the round ground pole. She was eventually able to jump a small cross rail.
I didn’t approach the problem head on. She taught me how to break complex tasks down into smaller and smaller steps until I found something she could do.
Over time she learned to compensate for the nerve damage. My vet warned me never to ride her. He told me it was just too risky. She might lose her balance and fall on top of me. I listened to him. I had seen her fall often enough to know he was right, but when she was ready, I rode her. She was the horse who introduced me to classical dressage. She was the first horse I taught to piaffe. It was because of her that I became balanced obsessed. That’s what kept her from falling. That’s what kept us both safe, and that’s what formed the core of everything I teach today.
Here is the simplicity of what she showed me:
Break complex tasks down into smaller, simpler components.
Find something – no matter how small, no matter how far away from your goal behavior it may seem to be – where you can get a “yes answer” response and begin there.
Build in small steps.
Build in repeating patterns.
At that time I didn’t know anything about clicker training. I didn’t have the clarity of the marker signal. I wasn’t talking about movement cycles or loopy training. I didn’t call any of what I was doing constructional training, but the elements were all there. I was primed to be a clicker trainer. And I was primed to be drawn to the language of constructional training that Goldiamond has given us.
The new book, “Modern Horse Training“, has grown out of those powerful lessons learned over forty years ago. What we have now are the words to describe what the horses have been showing us. Horses are truly our best teachers. We just need to listen to them and they will open their hearts and their wisdom to us.
The publication date for “Modern Horse Training” is April 26, 2023. I’ll share more about where it can be ordered as we get closer to the date.
Coming next: Contrast Teaches

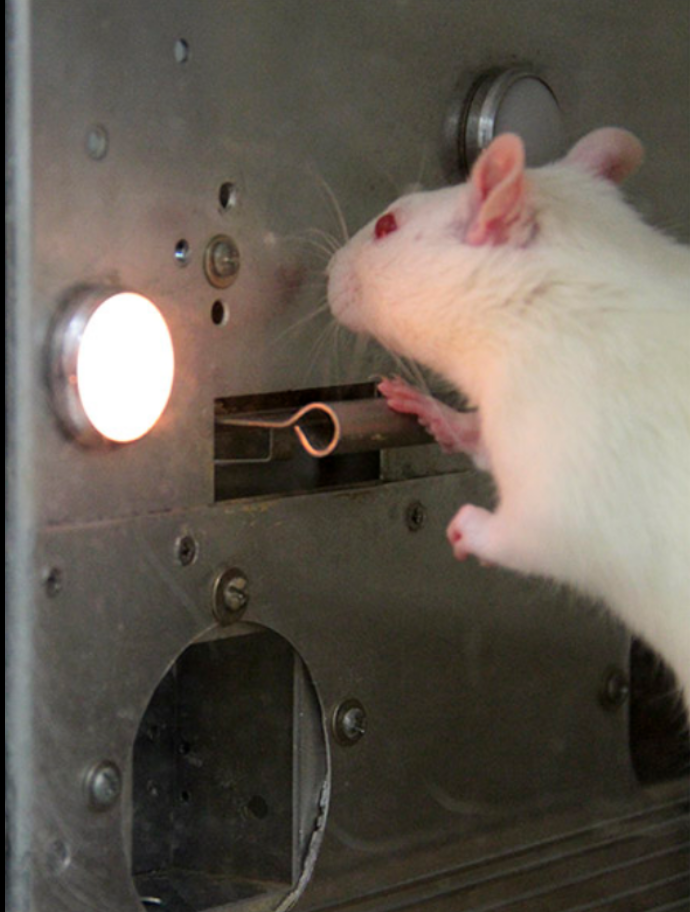 Here’s what that means: You are observing a rat that has been reinforced consistently for pressing a lever. Abruptly the lever pressing no longer produces the expected result.
Here’s what that means: You are observing a rat that has been reinforced consistently for pressing a lever. Abruptly the lever pressing no longer produces the expected result.